So, two things that happened in the past week that were of interest to me.
First, Saudi Arabia issued its official demands that the Qatari government would need to meet for the Saudis and their allies to end their diplomatic, political and economic blockade. With deep conditions ranging from the shuttering of the al Jazeera news service to a complete realignment of the country’s foreign policy from one of independent stances to something more appropriate to a province of Saudi Arabia.
Second, I spoke at PACOM in Hawaii about the changing nature of American power. The subsequent discussion focused heavily on the evolving role of the U.S. military as the country’s geopolitical priorities shift. The two neatly dovetail and highlight one of the deepening challenges the U.S. government faces in the next few years.
Let’s start with the background.
Near the end of World War II at the Bretton Woods conference the United States struck a deal with the allies. In the post-war order, the United States will defend not just your countries, but all your trade. You will no longer need to fight one another to access raw materials or markets. Furthermore, the American market — the only one of size to survive the war — will be open to you. All you have to do is side with America against the Soviets. Put simply, the United States pledged its military and economy to subsidize history’s largest alliance network.
By 1992, however, the Cold War had ended and — caught up in the transition from the Bush Sr administration to Clinton — the Americans neglected to craft a replacement strategy. The world changed, but U.S. strategic overwatch and subsidization of the alliance did not. All the various Cold War allies — ranging from the Germans to the Koreans to the Chinese to the Greeks — continued to benefit economically, but the Americans no longer received the strategic deference that was part of the original Bretton Woods deal.
Twenty-five years later, the economic cost of such an outdated strategy has led to the perception in many Americans’ minds that the world is freeloading on American security commitments. This isn’t intolerance or a fit of pique, it is a reasonable response to Washington’s inability to craft a replacement for a security policy that is a generation out of date. Such perceptions heavily colored the populist nature of the 2016 presidential election, and of course the election of Donald Trump — and now the American retrenchment is in full swing.
Yet it hardly started with Trump. American strategic policy has been on autopilot since 1992. The Clinton, W Bush and Obama administrations were too distracted, disinterested and/or unaware of the intricacies of the international system to meaningfully update the original Bretton Woods deal. In Donald Trump the Americans now have a leader just as distracted, disinterested and/or unaware as his three immediate predecessors. What is different about Trump is that as a populist he feels no attachment to the Bretton Woods system, so there is no natural inclination to just let-it-ride. Consequently, there are a growing number of breaches as the freshmen president, by action and inaction, peels away bits of the old system — but doesn’t replace them with anything new.
Such peeling is on full display with U.S. policy to the Persian Gulf. Trump’s first overseas visit wasn’t to traditional partners like Canada or Mexico or traditional allies like the United Kingdom or Japan, but instead to Saudi Arabia where Trump was quickly sucked into a gilded flattery fest of Trumpian proportions. The Saudis emerged from the visit-glow thinking they had the White House’s stamp of approval to restructure their region in whatever way they saw fit. Their first act wasn’t to move against ISIS or Iran, but Qatar — a tiny country the Saudis have long viewed as unnecessarily close to Iran, unnecessarily promiscuous when it comes to sponsoring political groups opposed to Saudi goals, and in general unnecessarily free-willed.
Qatar, however, didn’t buckle — and that brings us to PACOM.
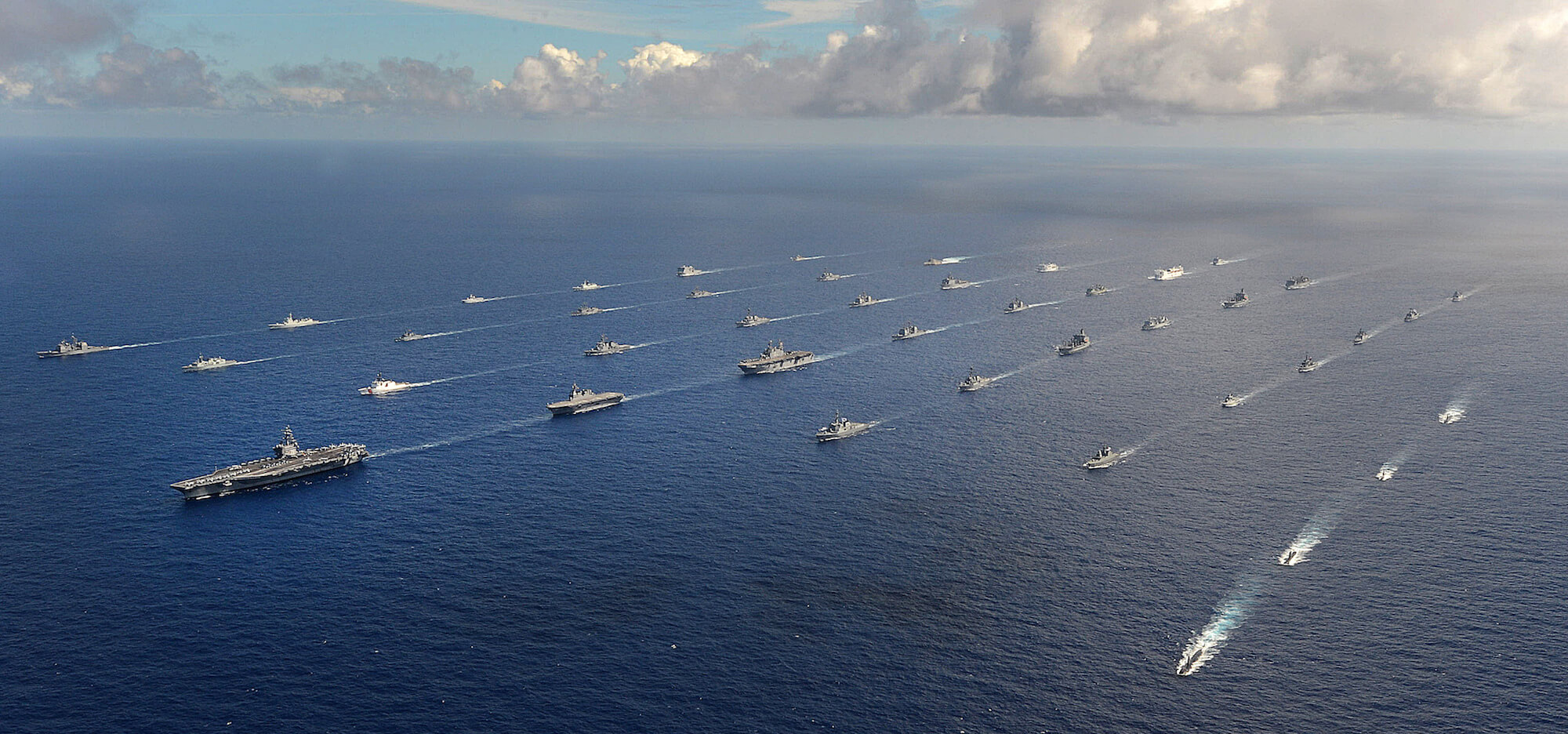
The U.S. military apparatus is charged with dispensing and enforcing U.S. strategic policy. As part of such duties, the military must constantly interact with allies and rivals around the world. That takes soldiers. Sailors. Marines. Airmen. Bases — and those bases require commitments to local and regional security concerns. That takes engagement, reliability, consistency. Every. Single. Day. By far the Americans’ largest overseas base these days is in Doha…the capital of Qatar. The CENTCOM base there has been the nerve-center for all US operations in Syria, Iraq and Afghanistan for some 15 years now.
The Qataris believe — correctly — that the U.S. military has their back and so there is no need for them to back down to the Saudis. The Saudis believe — correctly — that the Trump administration has green-lit their desire to restructure their region more to their liking. The Trump administration believes — correctly — that the U.S. strategic policy it inherited needs an overhaul, but has yet to craft that replacement policy.
The result in the U.S. military and diplomatic community is an overriding sense of confusion and frustration. Their standing orders are clear, but the shifts out of the White House are equally clear. And increasingly, the two contradict. The folks at PACOM can’t figure out, for example, whether they are supposed to treat China as a threat, a partner, a rising power who should be engaged…or given space. And mixed messages aren’t the best things when dealing with multiple aircraft carrier battle groups.
The issue is not so much Trump’s tendency to make policy via Twitter (although that obviously doesn’t help), but instead that ever since the Cold War ended the Americans have not had a goal.
Until the Americans select a new one they cannot have a coherent strategy. Until they have the national conversation required to select that goal, these deepening splits between needs and actions will only widen, leaving allies new and old not just in a lurch, but often acting against one another — as Saudi Arabia and Qatar are now.
There are plenty of places where this disconnect between emerging strategic interests and outdated policy will grind. Some of the louder ones include NATO, where it is no longer clearly in America’s interests to defend Europe against Russia. At the DMZ, where North Korea is far more a threat to South Korea, Japan and even China than it is to the United States. In the South China Sea where Chinese aggression is less a threat to American interests than to Taiwanese and Japanese. In Kuwait where America’s lack of oil import needs staggeringly reduces the Americans’ interest while staggeringly increasing Saudi belligerence. America’s use of Turkey’s Incirlik airbase will likely evaporate for a mix of reasons ranging from disenchantment with the evolution of the Turkish political space to a general feeling that the refugee issue is Europe’s problem, while Syria is Turkey’s problem.
Other places generate a lot less heartburn and — even without some new overarching strategy — are likely to keep their current levels of American involvement regardless. The UK, Canada and Australia have been and will remain America’s closest allies under almost any reasonable scenario. Morocco and Algeria are reliable partners in the struggle against Islamic militancy. Proximity and economic centrality will keep the Americans involved in Panamanian affairs for as long as water transport is a thing. Singapore sits on the world’s most strategically located real estate and is likely to be a valued partner until the end of time itself.
Perhaps the quirkiest aspect of all this are the countries likely to suffer the most from the policy discombobulation.
On the surface the Qatari-Saudi spat seems like it would deliver the Persian Gulf to Iran on a silver platter. But no. Within the first week of the argument, Turkey had deployed troops to its airbase in Qatar. Nothing is easy in the Middle East, even (especially!) for powers inhabiting the region. Turkey’s push to support Qatar is a clear indication to Tehran (and Riyadh) that even if US troops left the region tomorrow, Iran gets to look forward to facing off against yet another superior economic and military power. Unlike the United States, however, Turkey has a bevy of permanent regional interests directly opposed to Iran’s own, and occupies prime real estate in the neighborhood.
Trump’s wobbling on NATO seems like it gives the Russians everything they want — a Europe without the American security umbrella. But no. With the Americans out, the Germans have no choice but to rearm — and every time that has happened, it hasn’t turned out well for Moscow.
Loosening security ties with the East Asian rim seems like a dream come true for the Chinese. But no. Not only does that force Japan, Korea and Taiwan to massively bulk up their defense capacities (and perhaps go nuclear), but China’s extensive international economic position is utterly dependent upon the Americans keeping markets open and sea lanes safe on a global scale. Without America, there is no Chinese economic miracle — and most likely a naval war with Japan that China simply cannot win.
What will the Americans decide they want out of all of this? What will their new goal be? No clue. American politics are loud and messy and amped up with righteous indignation at present. Even if Americans could start the national conversation on finding that elusive goal today, I doubt they’d come up with the final answer in this presidency.