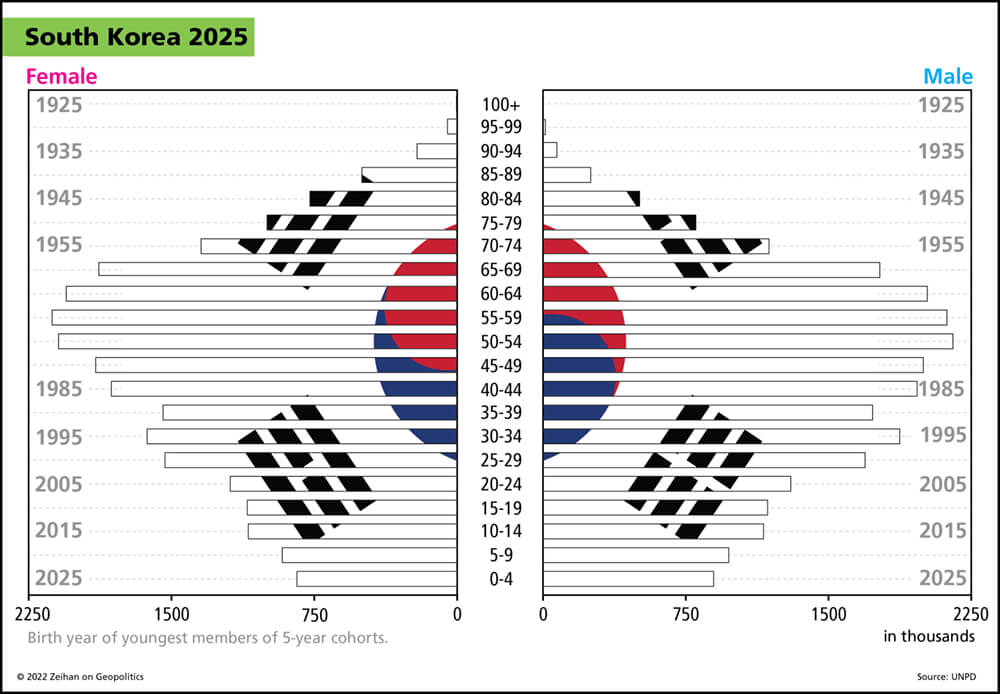
The US and South Korea have struck a deal for the US to help build nuclear-powered submarines for the Koreans. The US has kept this technology close to the chest for a long time, with the access list now a whopping two countries long: Australia and South Korea.
So, what does this mean for Seoul? Well, nuclear subs don’t exactly make sense for a conventional showdown with their neighbors to the North; however, the South Koreans have maintained the ability to quickly ramp up their nuclear industry. And the strategic implication of submarine-launched nukes accessible within a year really spices up the conversation.
Should the South Koreans be the first to topple the nuclear domino in Northeast Asia, you can bet your ass that everyone else will follow. How that plays out, nobody knows…but we probably won’t have to wait long to find out.
Transcript
Hey, all, Peter Zeihan here. Coming to you from Colorado. And today we’re talking about something that happened last week. We have a new agreement between the South Koreans and the Americans for the Americans to build and help build nuclear powered submarines for the South Korean Navy. And this is, really interesting. Now, the United States generally keeps a very tight lid on this technology was first developed in the 1950s, and it is the core for all of our ballistic and attack submarine fleets.
The big difference between a conventional sub and a nuclear sub is a conventional sub has basically service for every once in a while, and has a limited range and a limited duration of mission because it always has to come back and get more fuel. Whereas a nuke sub can basically stay under indefinitely and regularly, runs at least six month missions.
It’s really more an issue of the crew going completely batshit crazy because they’ve been underwater for so long, rather than a technical restriction. And of course, food stores, things like that.
To date, there’s only a half a dozen countries that have nuclear power subs. Most, obvious one is the United States, of course, and the only country recently that we have promised to assist with this technology, or the Australians and the Australians being basically a continent and being a long way away from anything that might be a security threat, it does make some security sense for them to have nuke subs, but for South Korea, South Korea, no.
South Korea is the size of Indiana, and its primary security threat is North Korea, which is right next door across the demilitarized zone. There is no, no, no military rationale for the South Koreans to develop a nuke sub to basically loiter nearby unless you see, nuke subs are good because you can do two things. Number one, you can strike from silence, but North Korea doesn’t have a functional navy, so who cares?
Or you can store a weapons platform offshore for months at a time. Now in a conventional fight with conventional missiles, an offshore sub is a very limited use. I mean, the United States, every once in a while launches some Tomahawks, but that’s like a once a year event, if that. And it’s not the sort of thing that would really change the math.
In a Korean conflict, but something to consider about the South Koreans is every few years they accidentally enrich some uranium up to near weapons grade levels. And then the IAEA, that’s the International Atomic Energy Commission, which is supposed to regulate nuclear technology, comes in, slaps the South Koreans on wrist, and they’re like, oh, sorry, that was accidental.
We’re never going to do that again. Then happens again a few years. Basically what the South Koreans have been doing for the last 40 years is making sure that if they ever need to, they can make a nuclear weapon on a relatively short time frame measured in weeks. And now, if they’re going to have nuclear powered subs, that means in a relatively short time, probably under a year, they could have nuke missiles on those subs.
What the South Koreans have now achieved is American sponsorship of what, in a few years, will now be a South Korean nuclear program. Whether this is good or bad really depends upon your point of view. The idea that the South Koreans need a deterrent versus North Korea. I mean, that makes a lot of sense. The idea that the South Koreans would like a way to go up to the Chinese and punch above their weight, that makes a lot of sense.
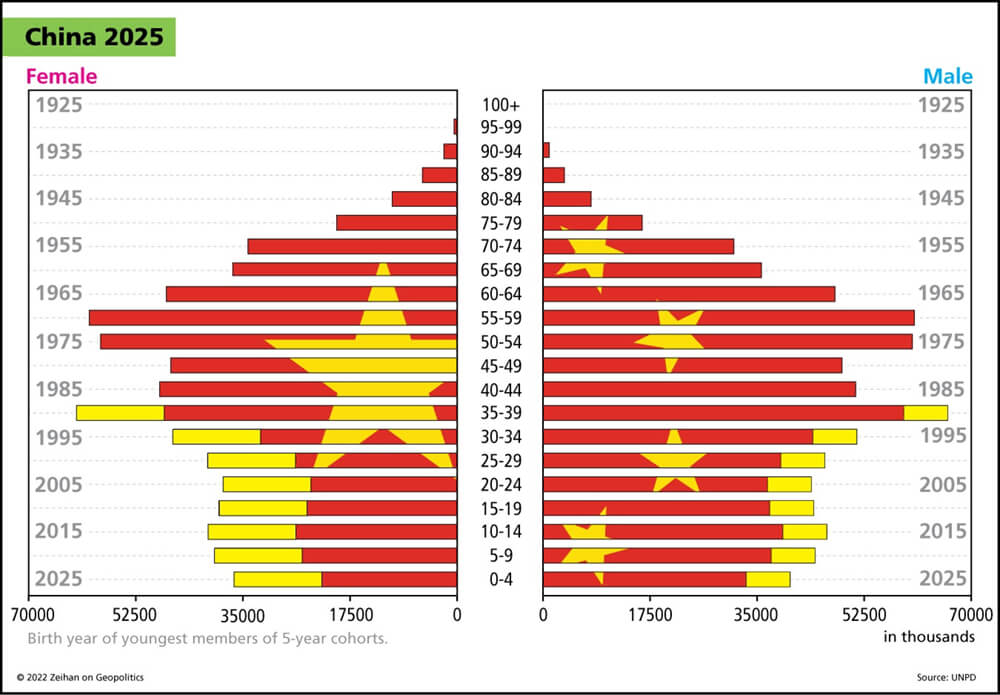
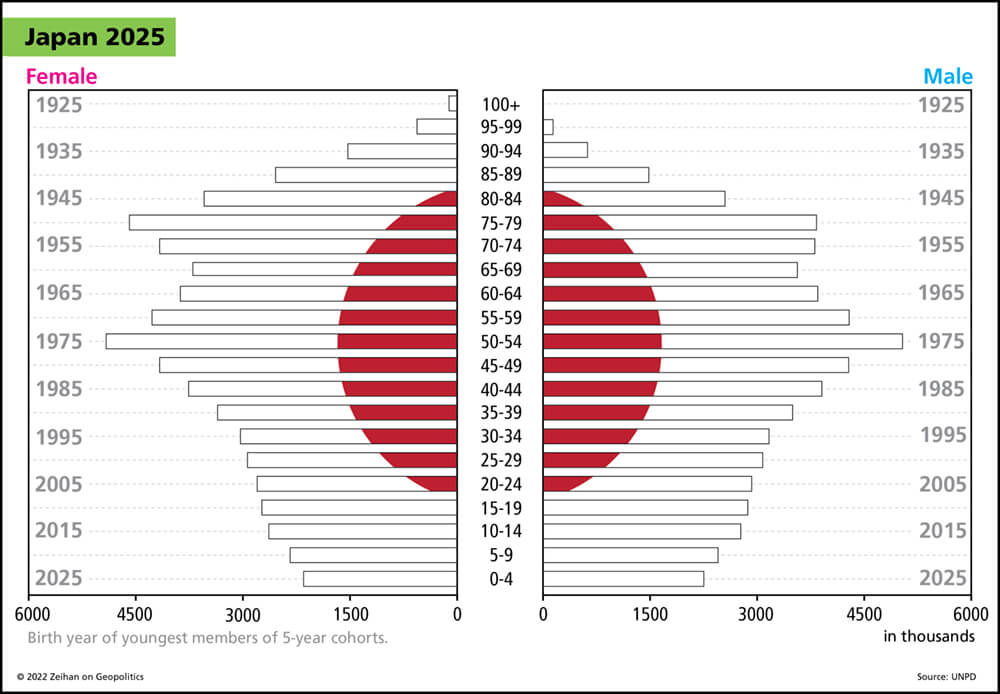
But there is no way that one country in Northeast Asia adds nukes to their arsenal, and the other countries don’t do the same thing. So I have always been concerned that when push comes to shove, it will be Japan that moves first, or Taiwan because of the threat of invasion. Now it looks like it might be the South Koreans, but as soon as one of them get them, the other two are going to have to have them.
So this decision might, from a certain monochromatic point of view, increase South Korean security, but it’s going to come at the cost of introducing an arms race to the broader region at the same time that the United States are stepping back, whether that is genius or pure idiocy is something that history will tell us. And maybe just within the next few years.