You’re about to watch a free video on the North Koreans getting involved in the Ukraine War, but before you do, learn how you can get access to the most recent videos and support a good cause in the process…
All proceeds for the remainder of this calendar year from all new subscriptions on Patreon between now and November 1, will be donated to MedShare International. That means you can get access to the daily videos, news digests, community forum and live Q&A, and your money will be going directly to support those in need.
You can click the link below to join us on Patreon or donate directly to help support MedShare’s efforts.
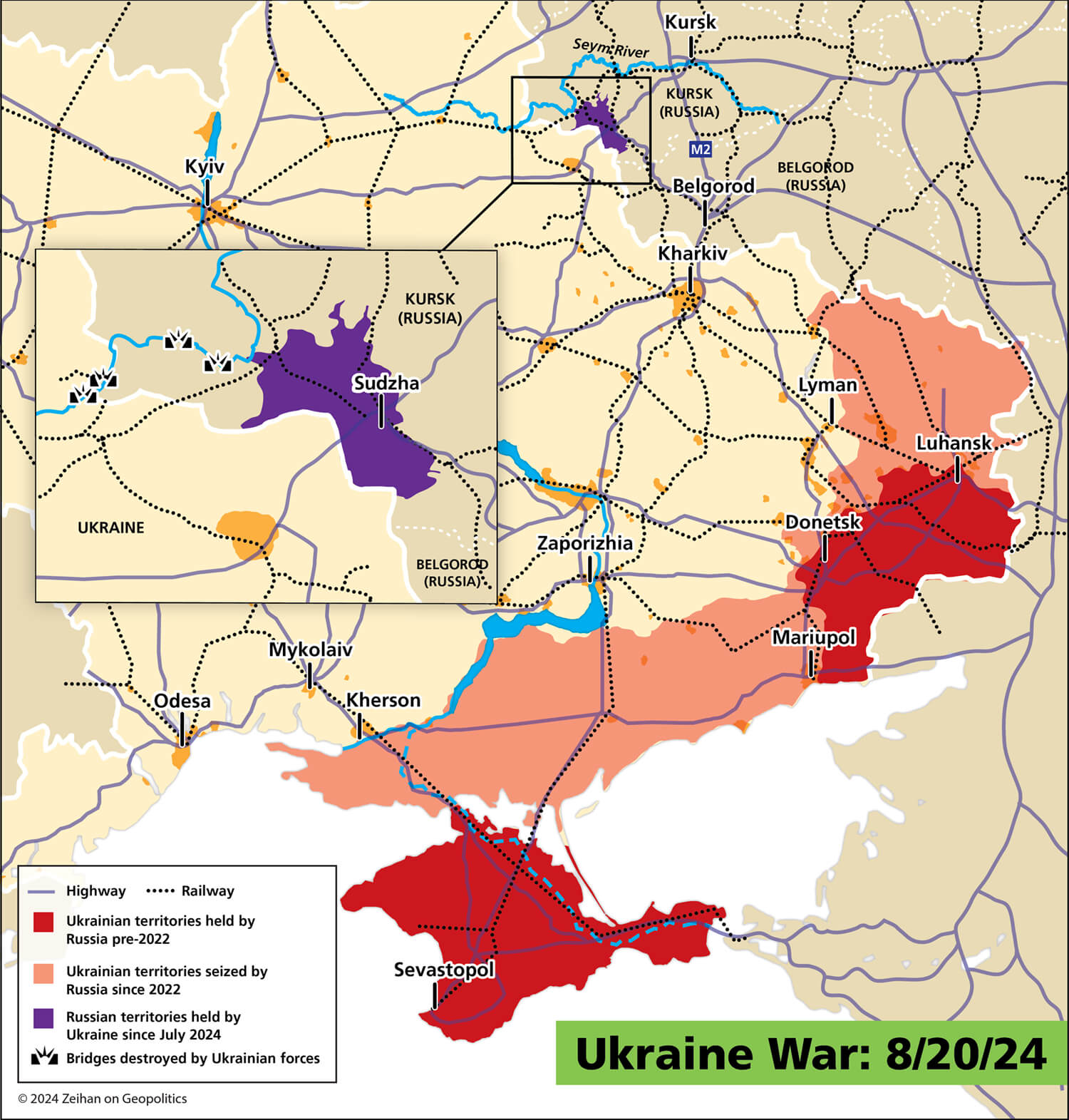
Reports coming out of South Korea indicate that North Korean troops could be deploying to Russia. These reports are unconfirmed, but the South Koreans aren’t usually in the business of lying. So, what does this mean for the Ukraine War?
North Korea hasn’t seen combat in ages, so while they gain some field experience, the rest of the world will get a glimpse at their capabilities. If the artillery and missiles the North Koreans already sent to the Russians are any indicator, I wouldn’t expect much. This could also drag the South Koreans into the conflict on the Ukrainian side, which might outweigh what the North Korea brings to the table for Russia.
Speaking of dragging new players into the war, Iran’s involvement with Russia could get Israel involved as well. This would likely come in the form of Israeli attacks on Iranian facilities making drones, but with Israel being a leader in defense technology, this could be a game changer for the Ukrainians.
The Russians are showing their declining military capacity by grasping at straws trying to get the North Koreans and Iranians to save their asses, but that strategy may soon backfire.
Here at Zeihan On Geopolitics we select a single charity to sponsor. We have two criteria:
First, we look across the world and use our skill sets to identify where the needs are most acute. Second, we look for an institution with preexisting networks for both materials gathering and aid distribution. That way we know every cent of our donation is not simply going directly to where help is needed most, but our donations serve as a force multiplier for a system already in existence. Then we give what we can.
Today, our chosen charity is a group called Medshare, which provides emergency medical services to communities in need, with a very heavy emphasis on locations facing acute crises. Medshare operates right in the thick of it. Until future notice, every cent we earn from every book we sell in every format through every retailer is going to Medshare’s Ukraine fund.
And then there’s you.
Our newsletters and videologues are free and we will never share your contact information with anyone. All we ask is that if you find one of our releases in any way useful, that you make a donation to Medshare. Over one third of Ukraine’s pre-war population has either been forced from their homes, kidnapped and shipped to Russia, or is trying to survive in occupied lands. This is our way to help who we can. Please, join us.
Transcript
Hey everybody. Peter Zeihan here coming to you from Colorado. Today there’s some weird stuff going in in the news. We’ve got reports that North Korean troops, are in the process of deploying to Russia. Some technical advisers are already there providing the Russians with assistance on how to use North Korean weaponry system. But now we’ve got, open discussion in South Korea about, intercepts.
From Point Yang, about, an actual troop deployment to maybe even fight on the front lines. Now, I don’t have any way to confirm this. I don’t have, my ear in the Korean dictator Kim Jong un’s, House or anything like that. But the South Koreans are not known for making stuff up. I mean, they’re known for.
And they’re known for bulgogi and kimchi and soju and electronics and cellular technologies and computing and mass manufacturing and heavy drinking. But they’re not known to make shit up. So I’m taking this a little bit more seriously than I would any other random report. We don’t usually get a lot of fake noise out of Seoul. Anyway. Four big things come from this.
Number one, the North Koreans have not been in a fight since 1953, so there is no living soldier in North Korea that is ever fired a rifle in anger. And getting any sort of information on how they might perform in real world circumstances would be an intelligence bonanza. Of course, it goes both ways. The North Koreans haven’t had been in a fight, so being able to see a front line, even if they’re not major combatants, is something that they could use for training purposes.
But for the point of view of the United States and South Korea, this is going to be the best bit of information we’ve ever had, in the last 70 years. That will allow us to remap our war plans, for the Korean Peninsula, should anything go wrong. Having a more accurate view of your enemy is always the first step, to planning.
The second big thing, North Korea is not the only country that is providing foreign assistance to the Russians. Specifically, they’re providing, ballistic missiles and artillery shells to the degree that maybe half of the artillery shells that have been used in Ukraine by the Russians this year are from North Korea. I mean, they’re crap. Probably half of them don’t work.
And they’ve been blowing up more Russian artillery tubes than Ukrainian artillery tubes, because sometimes they blow up too soon. Anyway, they’re not the only ones. The Iranians are also involved with the Shaheed drones, which over which a thousand have been used at this point. Now, just as in with the North Korean situation, there’s an intelligence bonanza to be had here or a way to get information on the inside of the system.
The Iranians, have recently launched a couple hundred ballistic missiles against Israel, and Israel is itching to respond, and they’ve basically already been given the green light, more or less, by the Biden administration to do so. The question is where, when and how? Well, if we now have the North Koreans intervening in the Ukraine war and we already have the Iranians intervening in the Ukraine war, then there’s an opportunity here for in exchange for the Biden administration, you know, kind of giving its blessing, to an Israeli retaliation attack on Iran.
They might just add a couple target coordinates in order to get the facilities that make the shitty drones. Iran, like North Korea, is not exactly a technological leader, and the number of personnel that can put these things together is relatively limited. So if you were to take out a cluster of technical support, which the Russians desperately need, as well as the manufacturing facilities of which the Russians desperately need, you could as part of your retaliation attack, see Israel actually remove a huge source of military capability from the Russians in the Ukraine war.
Also, keep in mind that the Russians are among the best in the world at assassination campaigns. And whenever an Iranian nuclear scientist gets a little bit too useful, they tend to meet a dire end. Just simply expanding that target set to include drone technicians is something the Israelis could do very, very, very easily. The third thing, as I mentioned, North Korea and Iran are not countries that I would mention as technological leaders and the fact that the Russians need them for half of their artillery shells and a substantial percentage of their drone warfare, that bodes really, really badly for the Russians ability to maintain this war long term.
We already know that they’re only be able to make a double digits number of new tanks a year. They’re just really refurbishing their old ones. And if the technical skills within the military industrial complex of Russia are down to the degree that they’re this dependent on two fourth string countries, that would suggest as we move forward, they’re going to become wholly dependent upon imports of weapons.
Well, that provides other opportunities for countries to choke the Russian war machine, because if the vulnerability isn’t in Siberia, if it’s inside this farm, that’s a lot easier to get to, especially if you’ve got countries like South Korea or Israel who are now involved. Which brings us to the fourth and final thing, South Korea, in Israel now involved, there’s a diplomatic angle here as well as a strategic angle.
You have to consider both of these countries have been desperate to avoid Ukraine’s entreaties, and the United States requests to get involved in the conflict in any meaningful way, because they’ve got bigger security issues closer to home. That focus wholly on them. And they didn’t want the Russians stirring the pot in their own backyards. Well, now the Russians are stirring the pot in their own backyard, so they are involved.
And so we’re seeing the political restrictions loosened in both Jerusalem and Seoul. And that can have a lot more impact than simply providing the Ukrainians with some technical help and some weapons systems. South Korea is one of the world’s five biggest arms exporters and produces regular things like artillery and rocket system and tanks that are not too far behind what comes out of Germany or France or the United States, but at a significantly lower price point.
In fact, they’ve already signed a deal to provide the poles with over a thousand tanks and assorted systems. Providing that sort of assistance to Ukraine is obviously a no brainer. But when you look at a country like Israel that has under 10 million people and is in kind of a tough neighborhood, mass producing hardware quickly is something they cannot do.
But the South Koreans can. And to flip the equation, the Israelis are the world leader or a world leader in anti-missile technologies and by far have the world’s best anti artillery and anti rocket technology and their Iron Dome system. Well, on day one of any theoretical Korean War, the North Korean is going to be lobbing all kinds of ammo into downtown Seoul.
So if Israel can help out Korea with artillery and rocket defense, cooperation between these two countries changes the strategic calculus of both of them in a very positive way. And if you can take Israel’s technical acumen on some specific weapons systems and married to Korea’s ability to produce a lot of things very quickly, you can actually see that working out through the entire Western alliance system.
So as I said several months ago, when the North Koreans started to get involved at Russian insistence, you know, this was probably one of the dumbest things that the Russians could do. I mean, yes, it gives them a tactical leg up in terms of ammo, but it risks bringing in a really important player. On the other side, and that’s South Korea.
And now we’re looking at both Israel and South Korea being brought in at more or less the same time and being brought in together. And that changes a lot.